Running Elasticsearch, FluentD, Kibana (EFK) on OKE
FluentD is the opensource data collector for unified logging layer. FluentD is CNCF graduated project. Kubernetes pods are frequently created, sometimes crash/fail and in some cases the nodes die or may go offline due to node pool upgrade. So the challenge is, as developers the log data is not preserved and not available for future analysis. Thus tools like FluentD becomes so handy for analyzing the logs.
EFK - Elasticsearch, FluentD and Kibana provides a good combination of opensource tool set for providing indexing ,storing and forwarding to nice visualization of viewing searchable logs on graphical user interface.
Since you need stateful storage and log files on the nodes needs to be captured and forwarded on your kubernetes cluster it is advisable to run the fluentD as daemonsets.
Installation
Here is the namespace.yaml
1kind: Namespace
2apiVersion: v1
3metadata:
4 name: kube-logging
Apply the above using the following command
1kubectl apply -f namespace.yaml
Here is the elasticservice_svc.yaml
1kind: Service
2apiVersion: v1
3metadata:
4 name: elasticsearch
5 namespace: kube-logging
6 labels:
7 app: elasticsearch
8spec:
9 selector:
10 app: elasticsearch
11 clusterIP: None
12 ports:
13 - port: 9200
14 name: rest
15 - port: 9300
16 name: inter-node
Apply the above yaml using the following command
1kubectl apply -f elasticservice_svc.yaml
Here is the es_statefulsets.yaml
1apiVersion: apps/v1
2kind: StatefulSet
3metadata:
4 name: es-cluster
5 namespace: kube-logging
6spec:
7 serviceName: elasticsearch
8 replicas: 3
9 selector:
10 matchLabels:
11 app: elasticsearch
12 template:
13 metadata:
14 labels:
15 app: elasticsearch
16 spec:
17 containers:
18 - name: elasticsearch
19 image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.5.2
20 resources:
21 limits:
22 cpu: 1000m
23 requests:
24 cpu: 100m
25 ports:
26 - containerPort: 9200
27 name: rest
28 protocol: TCP
29 - containerPort: 9300
30 name: inter-node
31 protocol: TCP
32 volumeMounts:
33 - name: data
34 mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
35 env:
36 - name: cluster.name
37 value: k8s-logs
38 - name: node.name
39 valueFrom:
40 fieldRef:
41 fieldPath: metadata.name
42 - name: discovery.seed_hosts
43 value: "es-cluster-0.elasticsearch,es-cluster-1.elasticsearch,es-cluster-2.elasticsearch"
44 - name: cluster.initial_master_nodes
45 value: "es-cluster-0,es-cluster-1,es-cluster-2"
46 - name: ES_JAVA_OPTS
47 value: "-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
48 initContainers:
49 - name: fix-permissions
50 image: busybox
51 command:
52 ["sh", "-c", "chown -R 1000:1000 /usr/share/elasticsearch/data"]
53 securityContext:
54 privileged: true
55 volumeMounts:
56 - name: data
57 mountPath: /usr/share/elasticsearch/data
58 - name: increase-vm-max-map
59 image: busybox
60 command: ["sysctl", "-w", "vm.max_map_count=262144"]
61 securityContext:
62 privileged: true
63 - name: increase-fd-ulimit
64 image: busybox
65 command: ["sh", "-c", "ulimit -n 65536"]
66 securityContext:
67 privileged: true
68 volumeClaimTemplates:
69 - metadata:
70 name: data
71 labels:
72 app: elasticsearch
73 spec:
74 accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
75 storageClassName: "oci"
76 resources:
77 requests:
78 storage: 100Gi
Apply the above yaml using the following command
1kubectl apply -f es_statefulsets.yaml
Here is the kibana.yaml
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: Service
3metadata:
4 name: kibana
5 namespace: kube-logging
6 labels:
7 app: kibana
8spec:
9 ports:
10 - port: 5601
11 selector:
12 app: kibana
13---
14apiVersion: apps/v1
15kind: Deployment
16metadata:
17 name: kibana
18 namespace: kube-logging
19 labels:
20 app: kibana
21spec:
22 replicas: 1
23 selector:
24 matchLabels:
25 app: kibana
26 template:
27 metadata:
28 labels:
29 app: kibana
30 spec:
31 containers:
32 - name: kibana
33 image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:7.5.2
34 resources:
35 limits:
36 cpu: 1000m
37 requests:
38 cpu: 100m
39 env:
40 - name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
41 value: http://elasticsearch:9200
42 ports:
43 - containerPort: 5601
Apply the above kibana.yaml using the below command
1kubectl apply -f kibana.yaml
Here is the fluentd.yaml
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: ServiceAccount
3metadata:
4 name: fluentd
5 namespace: kube-logging
6 labels:
7 app: fluentd
8---
9apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
10kind: ClusterRole
11metadata:
12 name: fluentd
13 labels:
14 app: fluentd
15rules:
16 - apiGroups:
17 - ""
18 resources:
19 - pods
20 - namespaces
21 verbs:
22 - get
23 - list
24 - watch
25---
26kind: ClusterRoleBinding
27apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
28metadata:
29 name: fluentd
30roleRef:
31 kind: ClusterRole
32 name: fluentd
33 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
34subjects:
35 - kind: ServiceAccount
36 name: fluentd
37 namespace: kube-logging
38---
39apiVersion: apps/v1
40kind: DaemonSet
41metadata:
42 name: fluentd
43 namespace: kube-logging
44 labels:
45 app: fluentd
46spec:
47 selector:
48 matchLabels:
49 app: fluentd
50 template:
51 metadata:
52 labels:
53 app: fluentd
54 spec:
55 serviceAccount: fluentd
56 serviceAccountName: fluentd
57 tolerations:
58 - key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
59 effect: NoSchedule
60 containers:
61 - name: fluentd
62 image: fluent/fluentd-kubernetes-daemonset:v1.4.2-debian-elasticsearch-1.1
63 env:
64 - name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_HOST
65 value: "elasticsearch.kube-logging.svc.cluster.local"
66 - name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_PORT
67 value: "9200"
68 - name: FLUENT_ELASTICSEARCH_SCHEME
69 value: "http"
70 - name: FLUENTD_SYSTEMD_CONF
71 value: disable
72 resources:
73 limits:
74 memory: 512Mi
75 requests:
76 cpu: 100m
77 memory: 200Mi
78 volumeMounts:
79 - name: varlog
80 mountPath: /var
81 - name: varlibdockercontainers
82 mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
83 readOnly: true
84 terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
85 volumes:
86 - name: varlog
87 hostPath:
88 path: /var
89 - name: varlibdockercontainers
90 hostPath:
91 path: /var/lib/docker/containers
Apply the above fluentd.yaml using the following command
1kubectl apply -f fluentd.yaml
Here is the list of all resources created under kube-logging namespace
1kubectl get all -n kube-logging
2
3NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
4
5pod/es-cluster-0 1/1 Running 0 1d
6
7pod/es-cluster-1 1/1 Running 0 1d
8
9pod/es-cluster-2 1/1 Running 0 1d
10
11pod/fluentd-kiju7 1/1 Running 0 1d
12
13pod/fluentd-hgt54 1/1 Running 0 1d
14
15pod/fluentd-kjhgh 1/1 Running 0 1d
16
17pod/kibana-6c98dcf5ff-huyjh 1/1 Running 0 1d
18
19
20NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
21
22service/elasticsearch ClusterIP None <none> 9200/TCP,9300/TCP 1d
23
24service/kibana ClusterIP 10.87.166.100 <none> 5601/TCP 1d
25
26
27NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
28
29daemonset.apps/fluentd 3 3 3 3 3 <none> 1d
30
31
32NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
33
34deployment.apps/kibana 1/1 1 1 1d
35
36
37NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
38
39replicaset.apps/kibana-uhyg6578j 1 1 1 1d
40
41
42NAME READY AGE
43
44statefulset.apps/es-cluster 3/3 1d
Here is the view of persistent volume it created
1
2kubectl get pv
3
4ocid1.volume.oc1.ca-xxx-1.yyy 100Gi RWO Delete Bound kube-logging/data-es-cluster-0 oci 1d Filesystem
5
6ocid1.volume.oc1.ca-xxx-1.yyy 100Gi RWO Delete Bound kube-logging/data-es-cluster-2 oci 1d Filesystem
7
8ocid1.volume.oc1.ca-xx-1.yyy 100Gi RWO Delete Bound kube-logging/data-es-cluster-1 oci 1d Filesystem
Once you confirm all the resources and pv's created then issue the following command to pull the grafana dashboard
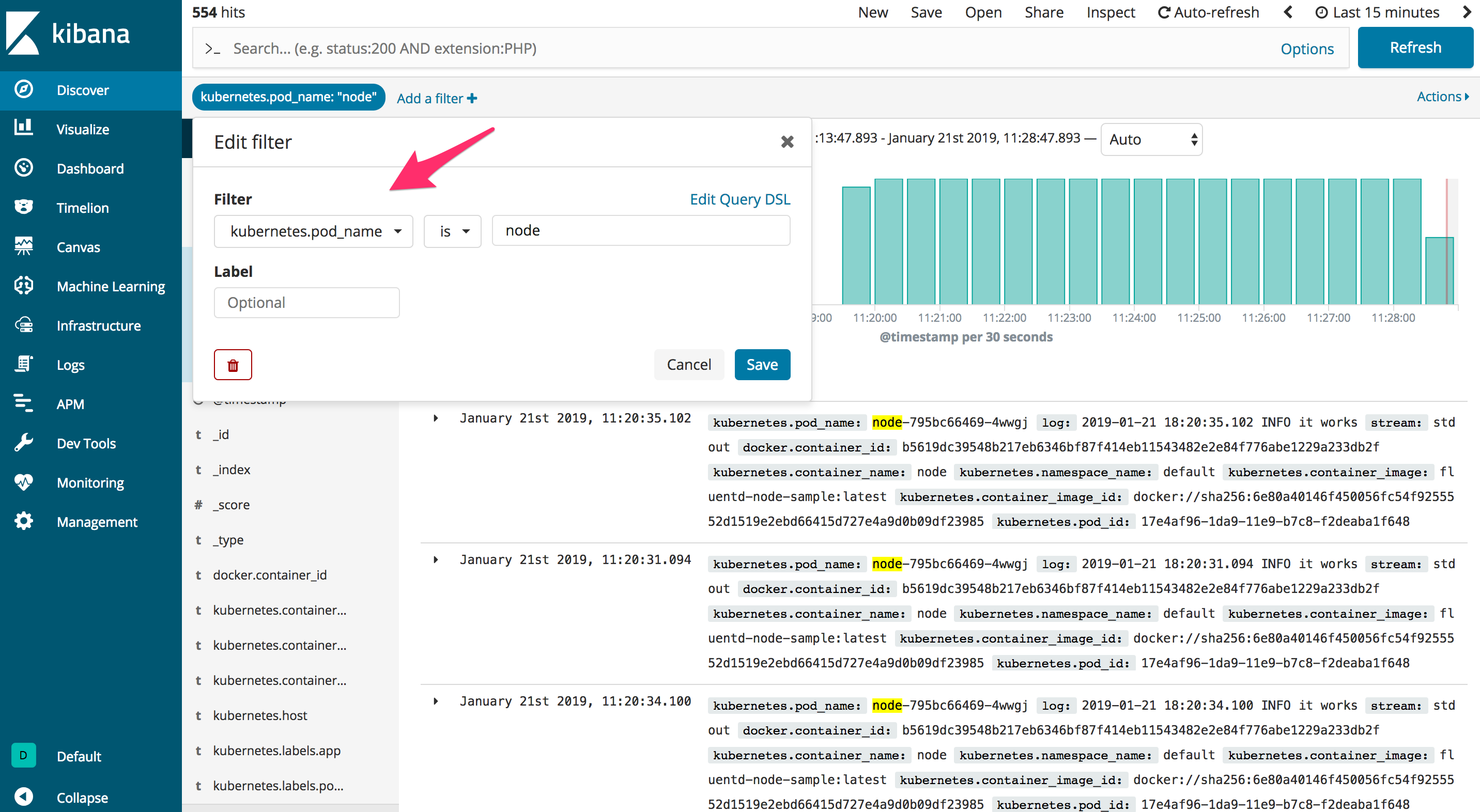
1kubectl -n kube-logging port-forward \$(kubectl -n kube-logging get pod -l app=kibana -o name) 5601:5601
To open the dashboard point the browser to http://localhost:5601